42 mathematica plotlabel position
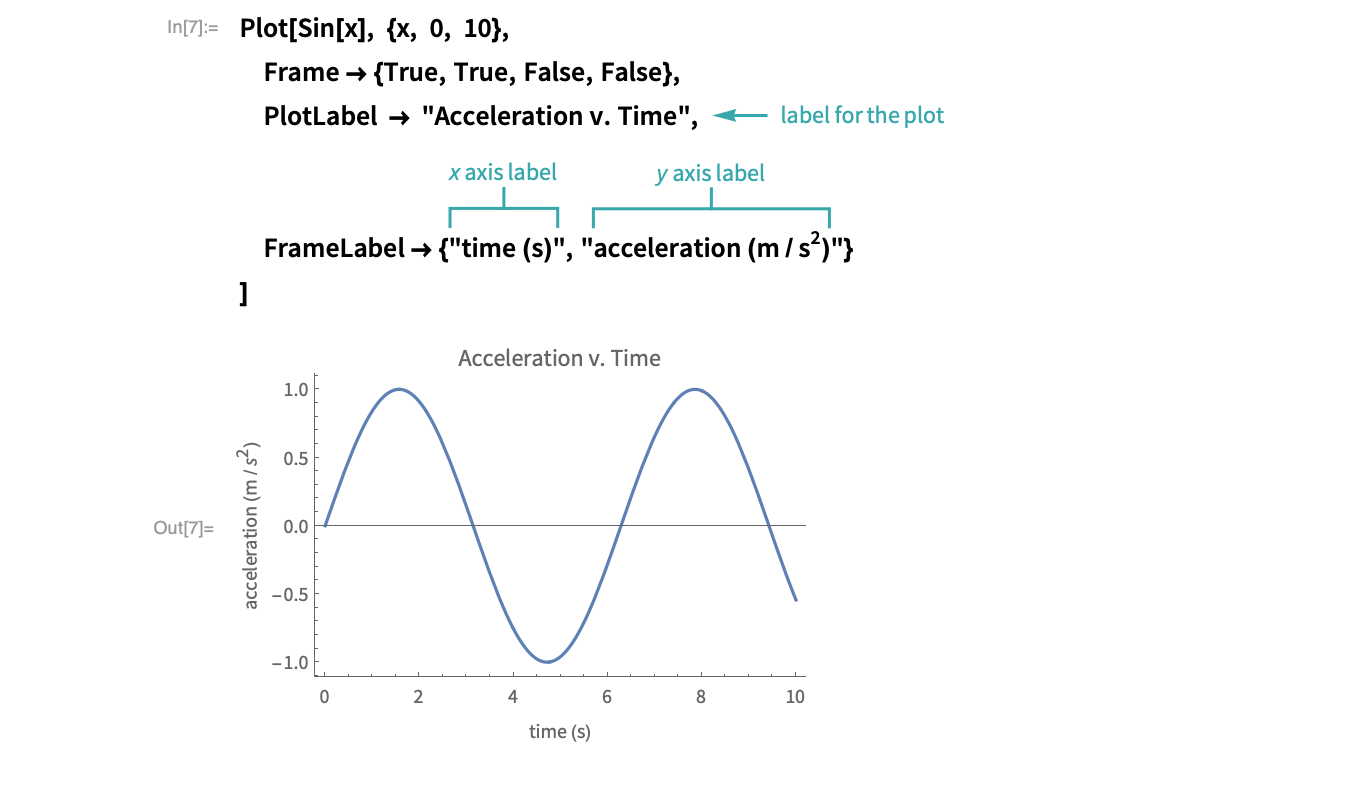
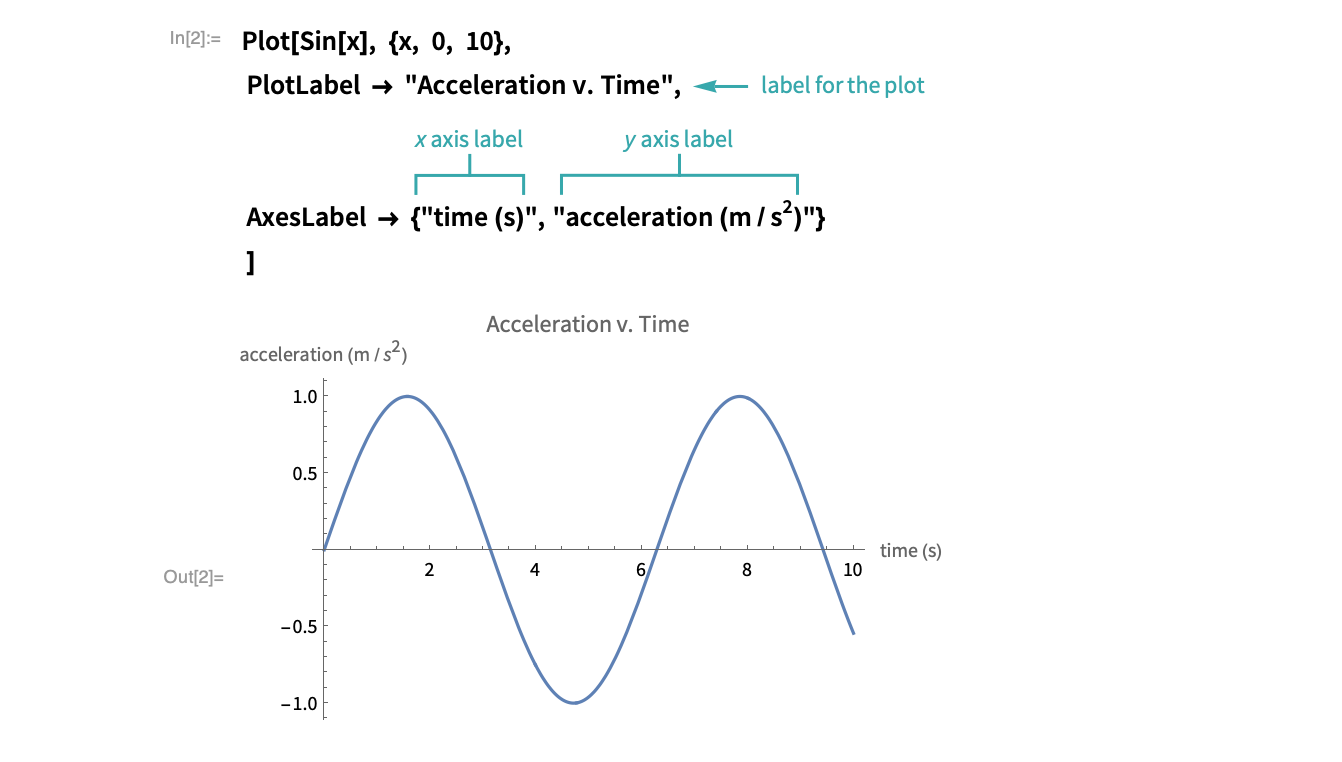
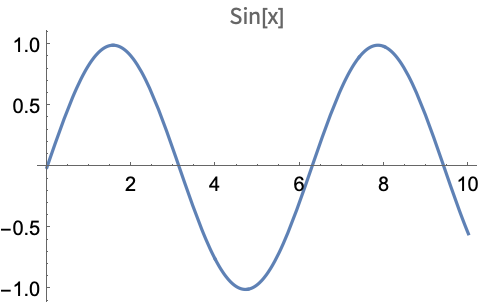
PDF PLOTTING AND GRAPHICS OPTIONS IN MATHEMATICA - Loyola University Chicago Now with axes labelled and a plot label : Plot x, x^2, x^3, x^4 , x, 1, 1 , AxesLabel x, y , PlotLabel "Graph of powers of x" -1.0 -0.5 0.5 1.0 x-1.0-0.5 0.5 1.0 y Graph of powers of x Notice that text is put within quotes. Or to really jazz it up (this is an example on the Mathemat-ica website) : PlotLabels—Wolfram Language Documentation PlotLabels. is an option for visualization functions that specifies what labels to use for each data source.
Use Placed to Position Labels: New in Mathematica 8 - Wolfram Use Placed to Position Labels: New in Mathematica 8, Graphics & Visualization, Use Placed to Position Labels, Use Placed to specify how labels should be positioned relative to the date and prices in a chart.

Mathematica plotlabel position
MATHEMATICA TUTORIAL, Part 1.1: Polar Plots - Brown University Polar Plots. We use polar coordinates as an alternative way to describe points in the plane. In polar coordinates, we describe points via their angle (called argument or polar angle) with the positive x -axis measured in counterclockwise direction, and the distance from the origin (called radial distance ). Labels—Wolfram Language Documentation Labels and callouts can be applied directly to data and functions being plotted, or specified in a structured form through options. Besides text, arbitrary content such as formulas, graphics, and images can be used as labels. Labels can be automatically or specifically positioned relative to points, curves, and other graphical features. wolfram mathematica - How can I constrain locators to a limited (but ... A list of three ordered pairs { { {minX, minY}, {maxX, maxY}, {dX, dY}}} is usually the key to determining the behavior of locators. {minX, minY} and {maxX, maxY} set the region. {dX, dY} sets the jump size: zero for unrestrained, any other positive number for the size of each hop.
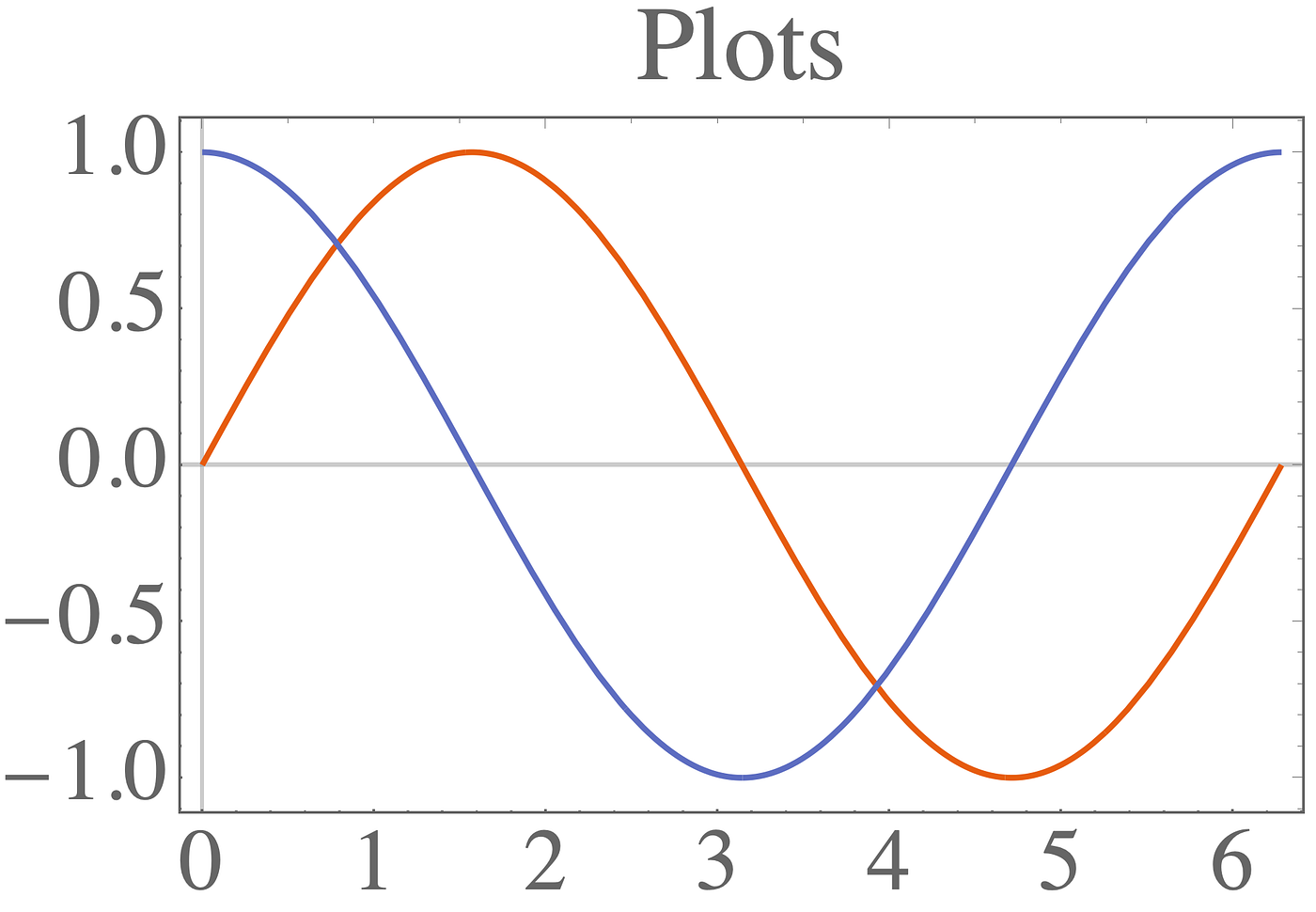
Mathematica plotlabel position. PDF MathPSfrag: LATEX labels in Mathematica plots Since Mathematica provides the means for en tering formatted expressions as part of ordinary text strings, the above example is somewhat artificial. The same effect could have been achieved by simply using PlotLabel→"χ2-test"and relying on Math- PSfrag (or to be more precise TeXForm) to produce the corresponding TEX representation. 7 tricks for beautiful plots with Mathematica - Medium It's possible to set individual sizes for each axis and the label, but it's easier to use BaseStyle to adjust it everywhere: plt = Plot [ {Sin [x], Cos [x]}, {x, 0, 2*Pi}, PlotLabel -> "Plots",... AxesLabel—Wolfram Language Documentation Place a label for the axis in 2D: In [1]:=, Out [1]=, Place a label for the axis in 3D: In [2]:=, Out [2]=, Specify a label for each axis: In [1]:=, Out [1]=, Use labels based on variables specified in Plot3D: In [1]:=, Out [1]=, Overall style of all the label-like elements can be specified by LabelStyle: In [1]:=, Out [1]=, Scope (2) The ParametricPlot and ParametricPlot3D commands in MATHEMATICA In this table, NN denotes a numerical value (which should be between 0 and 1 for Hue[NN]).The symbol BB can be one of the values True or False.And s 1 may include specifications such as Hue[NN] (setting curve color), AbsoluteThickness[NN] (setting curve thickness), or Dashing[{NN,NN}] (making the curve dashed). The modifier AspectRatio->Automatic gives the visually true proportions (where the ...
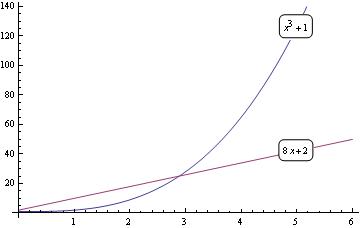
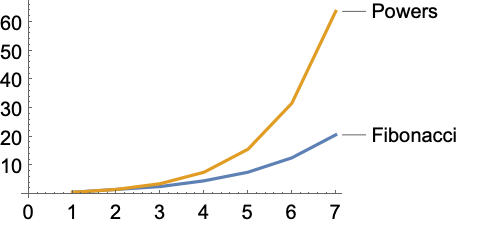
Mathematica: Labels and absolute positioning - Stack Overflow A simple example of placing text in mathematica is the following: Show [ Plot [x^3, {x, -1, 1}, Frame -> True, ImageSize -> Medium, FrameLabel -> {"x", "y"}, PlotRange -> { {-1, 1}, {-1, 1}} ], Graphics [ Text [Style ["A", Bold, 14, Red], {.5, .5}]] ] This places the letter A at the point (.5, .5) relative to the plot. PlotLabel—Wolfram Language Documentation Central infrastructure for Wolfram's cloud products & services. Software engine implementing the Wolfram Language. Instant deployment across cloud, desktop, mobile, and more. Technology-enabling science of the computational universe. Knowledge-based, broadly deployed natural language. Labels in Mathematica 3D plots - University of Oregon The first argument is the object to be displayed. The second argument is the position of the bottom left corner of the label. The third argument is a vector pointing in the direction along which the baseline of the label should be oriented. The length of this vector is taken as the width of the the label. Labeling curves in Mathematica - Lourenço Paz - Baylor University Labeling curves in Mathematica. Here is another quick tip about plotting curves using Mathematica. The option PlotLables can be used to identify curves. In our first example there are two curves named curve1 and curve2. a = Plot [x+7, {x, 0, 12}, PlotLabels->Placed [ {"curve1"}, Above]]
PDF Plot tutorial in Mathematica - University of Oregon Plot tutorial in Mathematica (updated for Mathematica v11) ... manually tweak the size and position of the legend until it looks good). Also, here we are manually setting the ticks on the plot, which is good to emphasize particular features of the functions. Play ... PlotLabel → "Two Magical ... matplotlib.axis.Axis.set_label_position — Matplotlib 3.6.0 documentation matplotlib matplotlib.afm matplotlib.animation matplotlib.animation.Animation matplotlib.animation.FuncAnimation matplotlib.animation.ArtistAnimation labeling different plots in the same graph in Mathematica 8 You can label the lines as you like using this method, based on my earlier post here. After labelling, the plot without dynamic content can be found set to plainplot. It works by turning each line into a self-labelling button. You can modify labels for different labels. Specify Label Locations: New in Wolfram Language 11 Specify Label Locations. A callout can be given a specific location and anchor point with both x and y coordinates. In [1]:=. Out [1]=. Labeled can be given an x coordinate and a relative position. In [2]:=.
How to Adjust Axis Label Position in Matplotlib - Statology You can use the following basic syntax to adjust axis label positions in Matplotlib: #adjust y-axis label position ax. yaxis. set_label_coords (-.1, .5) #adjust x-axis label position ax. xaxis. set_label_coords (.5, -.1) . The following examples show how to use this syntax in practice.
Label a Plot—Wolfram Language Documentation The Wolfram Language provides flexible options for labeling plots, allowing you to present ideas more clearly in presentations and publications. There are several methods of adding a label to a plot. You can use PlotLabel, Labeled, or interactively add text to a plot using Drawing Tools. For a description of adding text to plots using Drawing ...
plotting - How to change the position of the PlotLabel? - Mathematica ... PlotLabel positions the label on top of the plot by default. I would like to put it below the plot. How can I do that? Thank you.
Label a Plot—Wolfram Language Documentation Software engine implementing the Wolfram Language. Wolfram Universal Deployment System. Instant deployment across cloud, desktop, mobile, and more. Wolfram Science. Technology-enabling science of the computational universe. Wolfram Natural Language Understanding System. Knowledge-based, broadly deployed natural language.
Placed—Wolfram Language Documentation represents an expression expr placed at relative position pos in a chart or other display. Placed [ { e1, e2, … }, pos] places each of the e i at a relative position specified by pos. Placed [ { e1, e2, … }, pos, f] applies the function f to each of the e i before displaying it. Details, Examples, Basic Examples (4)
MATHEMATICA TUTORIAL, Part 1.1: Direction Fields - Brown University It require vector-valued input: one for abscissa (usually labeled by x or t) and another for ordinate. Therefore, to plot a direction field for a first order differential equation d y / d x = f ( x, y), a user needs to set 1 for the first coordinate and f ( x,y) for the second one, so making the vector input ( 1, f ( x, y)).
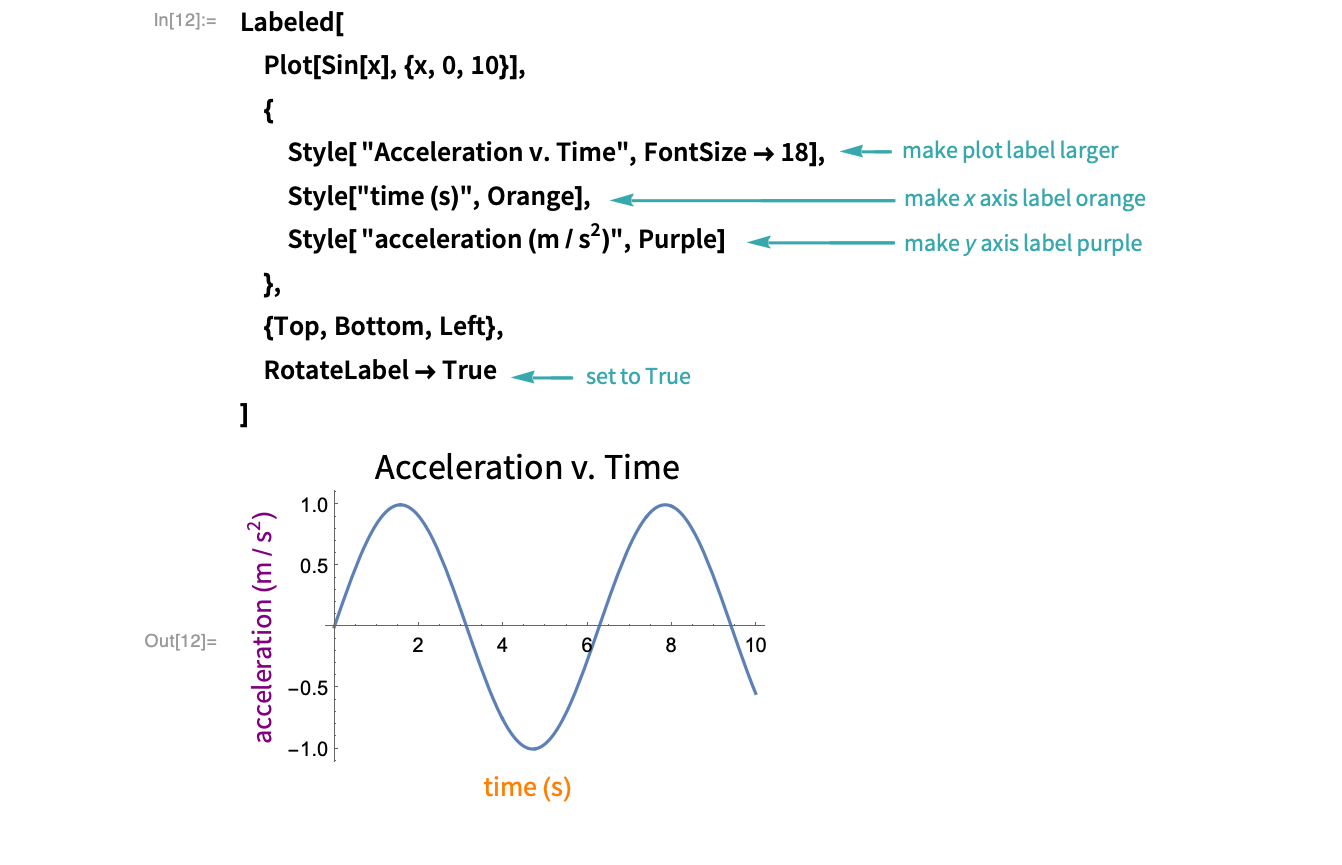
How to rotate AxesLabel - narkive From the. online help, "RotateLabel is an option for twoâ dimensional graphics. functions which specifies whether labels on vertical frame axes should. be rotated to be vertical." For example, In [1]:=. Plot [Sin [x], {x, -2*Pi, 2*Pi}, Frame -> True, FrameLabel -> {"x-axis", "This is the function sin x"},
plotting - How to change the position of axes label? - Mathematica ... ParametricPlot [ {4 Cos [θ] - 2 Sin [θ]^2, 3 Sin [θ] + 2 Cos [θ]^2}, {θ, 2.1, 10}, PlotStyle -> { {Thin, Dashed, Black}}, Frame -> True]; Labeled [%, {"Q/k", "N/k"}, {Left, Bottom}] See also: Placing x-axes label below rather than at end of axes, Position of axes labels, Positioning axes labels,
(PDF) Engineering Vibration Fourth Edition - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
wolfram mathematica - How can I constrain locators to a limited (but ... A list of three ordered pairs { { {minX, minY}, {maxX, maxY}, {dX, dY}}} is usually the key to determining the behavior of locators. {minX, minY} and {maxX, maxY} set the region. {dX, dY} sets the jump size: zero for unrestrained, any other positive number for the size of each hop.
Labels—Wolfram Language Documentation Labels and callouts can be applied directly to data and functions being plotted, or specified in a structured form through options. Besides text, arbitrary content such as formulas, graphics, and images can be used as labels. Labels can be automatically or specifically positioned relative to points, curves, and other graphical features.
MATHEMATICA TUTORIAL, Part 1.1: Polar Plots - Brown University Polar Plots. We use polar coordinates as an alternative way to describe points in the plane. In polar coordinates, we describe points via their angle (called argument or polar angle) with the positive x -axis measured in counterclockwise direction, and the distance from the origin (called radial distance ).















Komentar
Posting Komentar